As climate change accelerates, agriculture faces growing challenges: extreme weather events like droughts, floods, and wildfires reduce productivity, while many regions lack the capacity to adapt. At the same time, food demand is projected to rise dramatically—reaching an estimated 9 billion people by 2050. The solution? Implementing Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) to ensure sustainable food production and build resilience to environmental pressures.

Figure1: Climate-Smart Agriculture (Source: https://eos.com/blog/climate-smart-agriculture/)
CSA is an integrated approach that uses sustainable farming technology to achieve two critical goals: secure food production and combat climate change. By applying precision agriculture techniques, CSA focuses on three key pillars:
Climate change doesn’t just affect crop yields; it fundamentally disrupts agricultural systems:
Invasive pests thrive in environments altered by global warming and trade. The consequences include:

Figure 2: Effects of temperature rise on pests. (Source: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4450/12/5/440)
• New disease threats: Many pests act as vectors, spreading pathogens that harm crops.
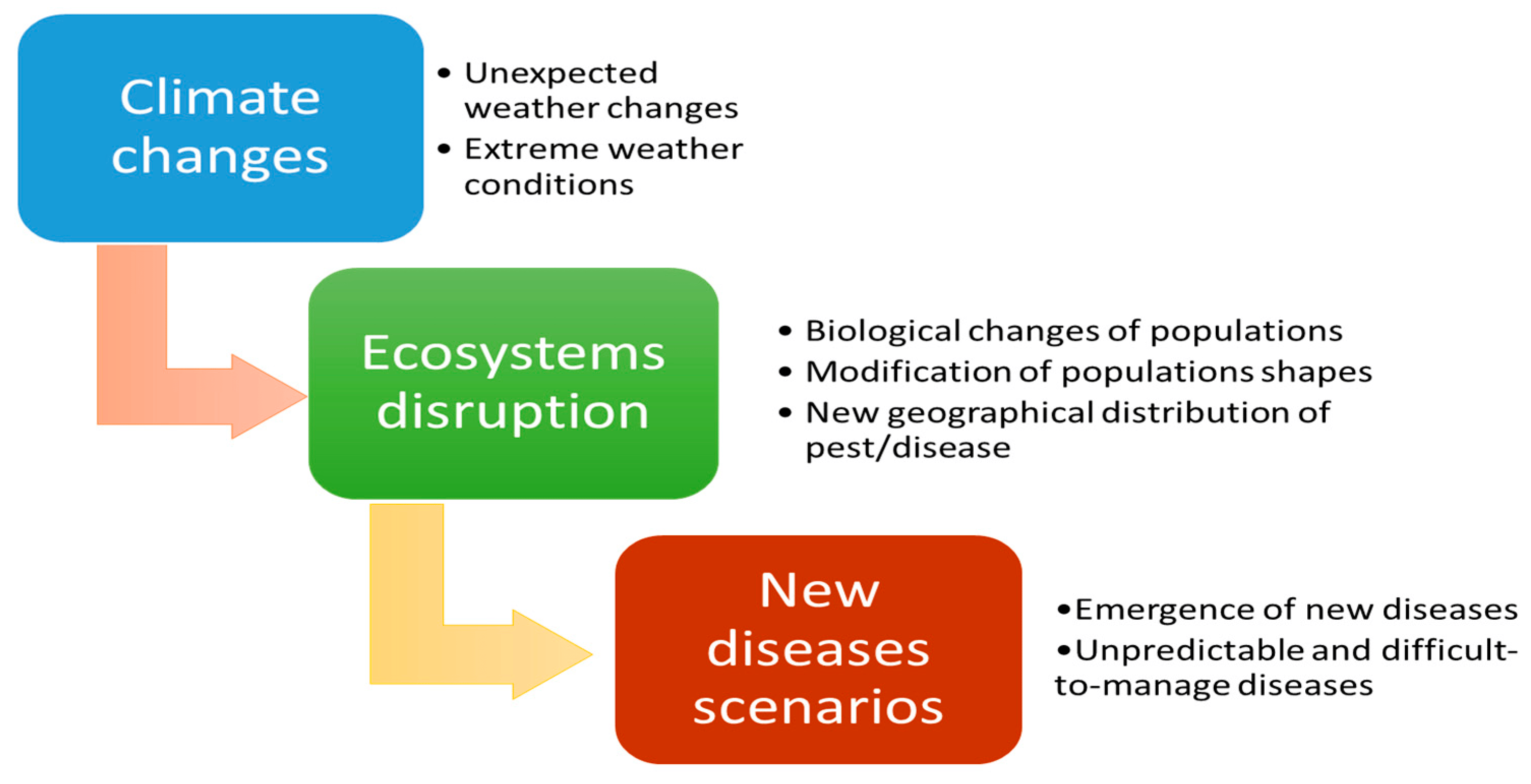
Figure 3: Relation between climate changes and new plant disease scenarios (Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369051521_Climate-Smart_Pest_Management_in_Sustainable_Agriculture_Promises_and_Challenges)
• Serious phytosanitary problems: In regions where pest management systems are unprepared and the natural predators or parasitoids of the pest is not yet present, invasive pests can cause significant damage, impacting food security and local economies.
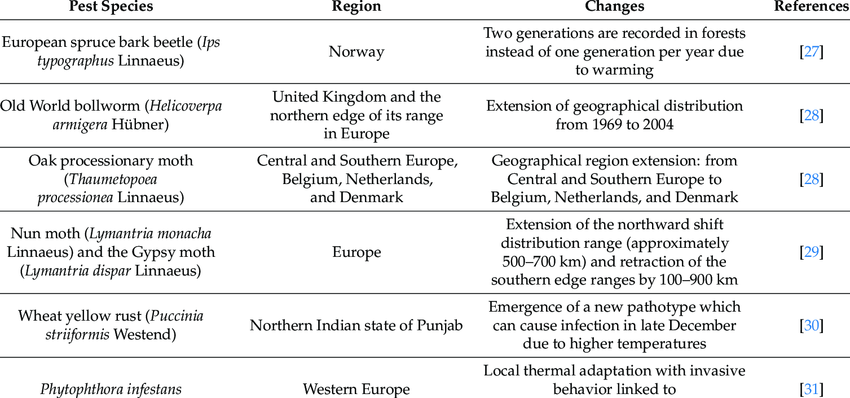
Figure 4: Examples of climate change impact on plant pests (Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369051521_Climate-Smart_Pest_Management_in_Sustainable_Agriculture_Promises_and_Challenges)
Advancements in precision agriculture are driving the development of Climate-Smart Agriculture. By integrating AI, IoT, and real-time data analytics, farmers can implement more effective, low-impact pest management strategies.
Early Diagnosis
Risk Assessment and Forecasting
Figure 5: The Internet of Things (Source: https://www.cyberdb.co/an-internet-of-things-technology-current-tendencies-in-iot-outsourcing/)
Effective Interventions

Figure 6: Pyramid of the Climate Smart Pest Management (CSPM) main processes in sustainable farming sístem (Source: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369051521_Climate-Smart_Pest_Management_in_Sustainable_Agriculture_Promises_and_Challenges)
Climate change and global trade are accelerating the spread of invasive pests and pathogens, threatening agriculture worldwide. Regions without established pest management systems are particularly vulnerable.
CSA offers a sustainable solution by focusing on:

Figure 7: Climate-Smart Agriculture (https://naturenews.africa/climate-change-environmentalist-tasks-farmers-on-adoption-of-climate-smart-agricultural-techniques/)
By leveraging AI, IoT, and data analytics—cornerstones of precision farming—CSA reduces reliance on chemical pesticides, protects biodiversity, and promotes long-term agricultural sustainability.
To secure food production for future generations, CSA is the way forward—bridging productivity and environmental responsibility.