Codling moths (Cydia pomonella) can wreak havoc on crops like apples, pears, pistachios, almonds, and grapes, making codling moth control a top priority for orchardists. But with so many codling moth trap options available, choosing the right one can feel overwhelming.
This guide breaks down the best codling moth traps for apple trees and other crops, comparing them based on orchard size, budget, ease of use, sustainability, and ROI—helping you make the best decision for your farm.
First, let’s talk about the Life Cycle of the codling moth. Understanding the codling moth’s life cycle and recognizing the signs of infestation are essential steps in implementing effective control measures to protect your orchard. Keep in mind that the damaging stage is the larval. The stages of its life cycle are:
🔬 Curious about insect life cycles? Check out our article on the different stages of insects, from egg to adult: Insect Metamorphosis 🐛🦋
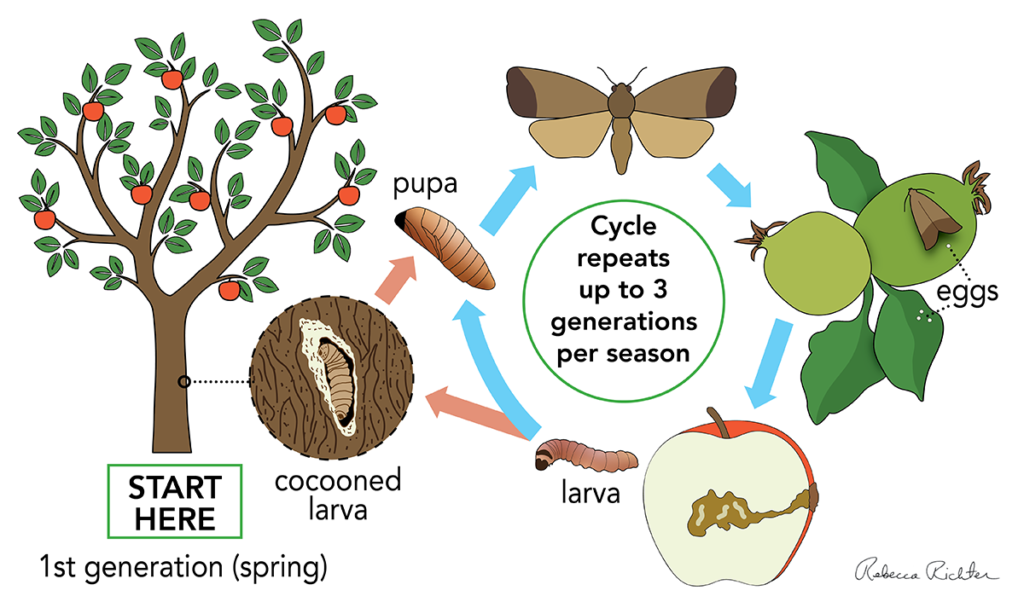
The Life Cycle of the Codling Moth
Source: https://agresearch.montana.edu/warc/guides/apples/managing_codling_moth_in_the_home_orchard.html
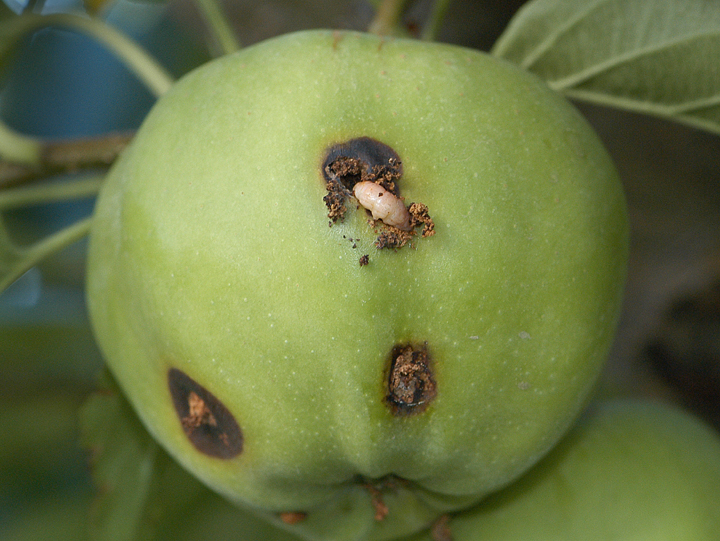

Codling moth larva exiting fruit to pupate (E. Beers, July 2007)
Source: https://treefruit.wsu.edu/crop-protection/opm/codling-moth-1/
| Trap Type | Best For | Ease to Use | Sustainability | Time-saving | Accuracy | ROI |
| Pheromone Traps | Monitoring and early detection | Easy | Eco-friendly | Low | Low | Low |
| Light Traps | Broad moth capture | Requires power | May trap beneficial insects | Low | Medium | Medium |
| Automated Digital Traps | Data-driven pest management | Simple setup, remote monitoring | Reduces pesticide use | High | High | High |

Pheromone Trap
Source: https://www.khethari.com/blogs/news/step-by-step-guide-to-setting-up-pheromone-traps
🔹 Best for: Small to medium orchards looking for cost-effective monitoring
💰 Cost: Low
🛠️ Ease of use: Simple setup, requires regular lure replacement
🌱 Sustainability: Highly eco-friendly
Pheromone traps are the most widely used codling moth traps for apple trees and other orchard crops. These traps attract male moths using synthetic sex pheromones, reducing mating and controlling populations.
✅ Pros:
⚠️ Considerations:
🚀 Best Use Case: If you’re looking for a simple and cost-effective monitoring tool, pheromone traps are your best bet.
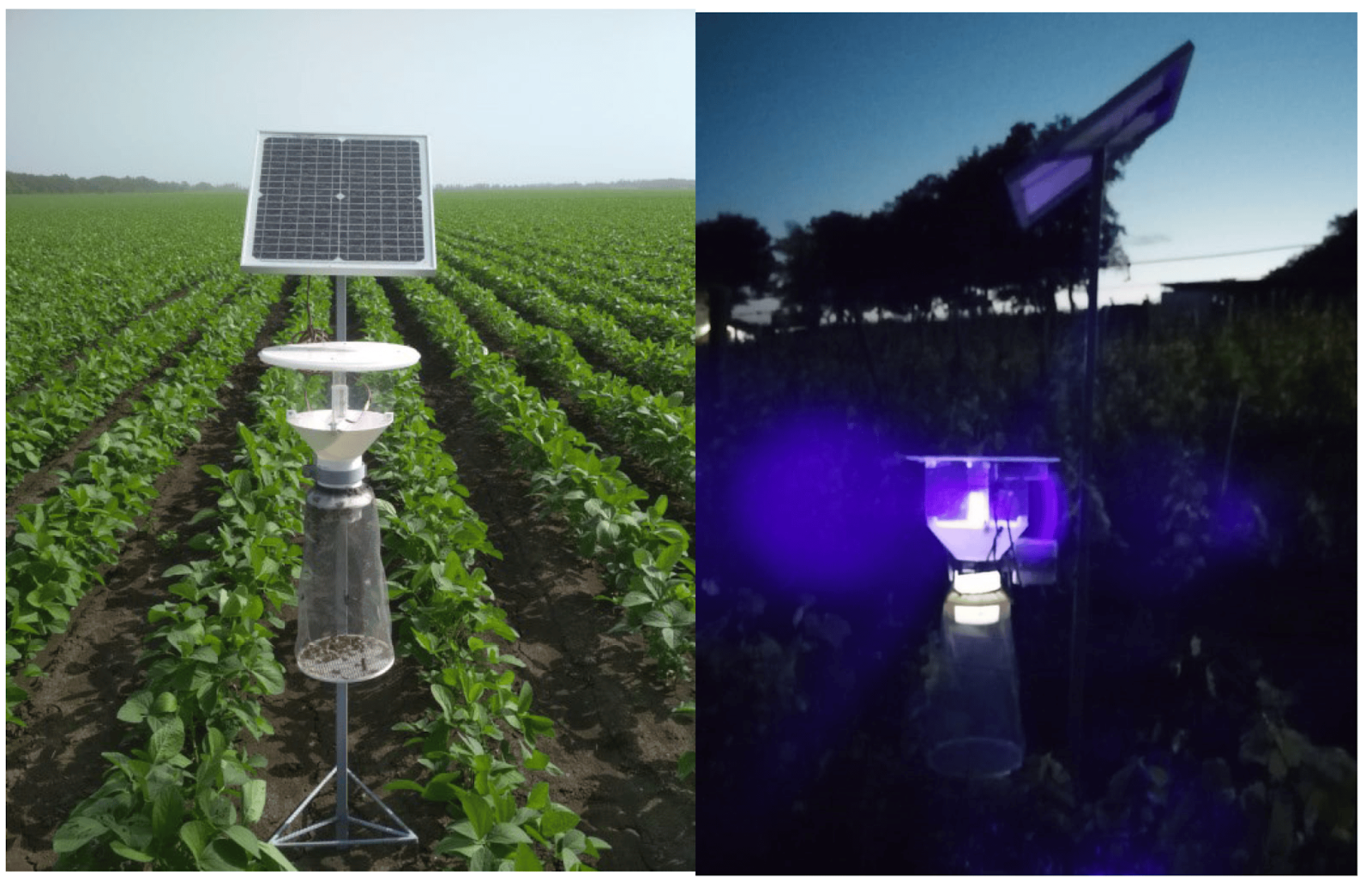

Light Trap
🔹 Best for: Medium to large orchards with non-chemical control goals
💰 Cost: Medium
🛠️ Ease of use: Requires power source
🌱 Sustainability: No chemicals, but may impact beneficial insects
Light traps use specific wavelengths of UV light to attract moths and trap them in a container or sticky pad. These traps capture both male and female moths, making them useful for population reduction.
✅ Pros:
⚠️ Considerations:
🚀 Best Use Case: Ideal for growers seeking chemical-free codling moth control but who can manage the energy requirements.

Automated Digital Trap
Source https://scoutlabs.ag
🔹 Best for: Large orchards or tech-savvy growers wanting real-time pest monitoring without the use of pesticides
💰 Cost: Long-term savings outweigh the initial purchase
🛠️ Ease of use: Simple setup, remote monitoring
🌱 Sustainability: Reduces pesticide use and labor costs
📈 Labor costs are rising! Learn why and how digital traps can save you time, money, and improve accuracy: Read more here 🚜🤖
✅ Pros:
⚠️ Considerations:
🚀 Best Use Case: If you’re managing a large orchard and want precision pest control, AI-powered traps are a game-changer. Unlike traditional methods that require frequent manual monitoring, digital traps provide real-time data and reduce unnecessary pesticide applications, ultimately saving time and money.
🔎 Check out our previous article for an in-depth guide on insect traps: Insect Traps Explained – A Practical Guide for Effective Pest Control 🚜🐛
Selecting the most suitable trap depends on various factors, including your orchard’s size, pest pressure, and management goals. Here are some considerations to guide your decision:
To maximize the effectiveness of your chosen traps, consider the following best practices:
🔎Want to level up your pest control strategy? Check out our previous article on Integrated Pest Management (IPM): 3+1 Tips for Successful IPM 🐛🚜
Choosing the right codling moth trap depends on your orchard size, budget, and sustainability goals. The best results often come from combining different traps within an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategy.
💡 Pro Tip: Even if you start with pheromone traps, keep an eye on new technologies—AI-powered traps are becoming more accessible and could revolutionize your approach to codling moth control in the near future!
📩 Have questions? Talk with us — we’re here to help! 🍏🐛