Farming is changing.
Pests are getting smarter, and consumers want healthier, eco-friendly food.
But here’s the challenge: chemical pesticides are losing their edge.
That’s where biopesticides step in. They:
✔ Work with nature, not against it, targeting pests without affecting beneficial insects or soil health.
✔ Help slow pesticide resistance by using natural mechanisms that make it much harder for pests to develop resistance.
In a nutshell: An effective protection without the downsides!
🔍 In today’s blog, we will cover:
✔ What biopesticides are & how they work
✔ Real biopesticides examples you can use
✔ Best practices for applying biopesticides
✔ How to decide if they’re the right fit for your orchard
Biopesticides are pest control products derived from natural sources like plants, bacteria, and fungi. Instead of relying on synthetic chemicals, they use nature’s own defenses to target specific pests while minimizing harm to beneficial insects, humans, and the environment.

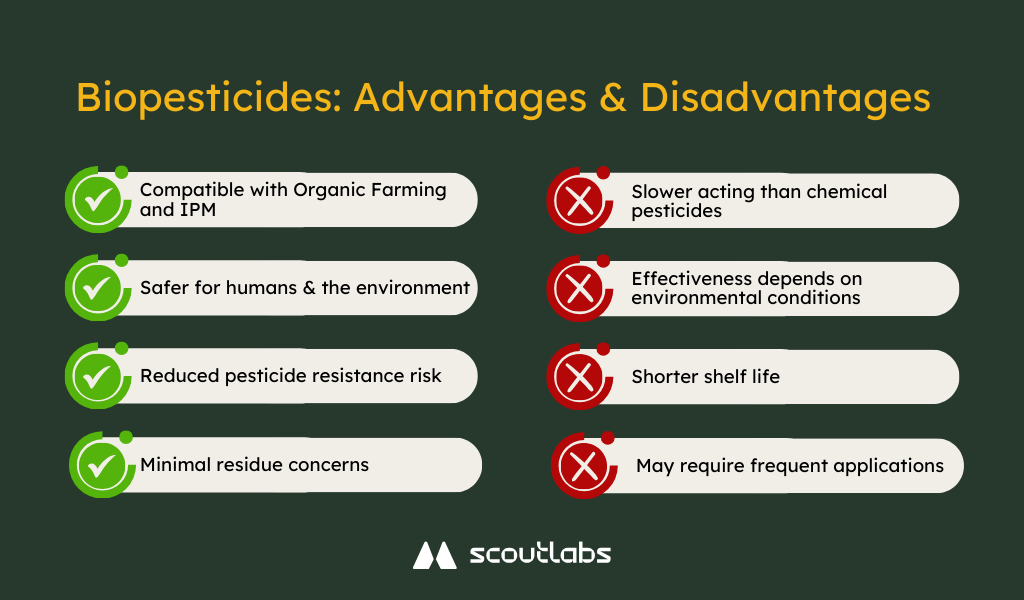
Biopesticides make pest control more sustainable, safer, and smarter, but they do come with challenges.
✅ Compatible with Organic Farming and Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Organic farming is gaining momentum, and biopesticides fit perfectly into this approach, as well as with IPM strategies, reducing reliance on synthetic chemicals.
✅ Safer for us and the environment
Unlike synthetic pesticides, biopesticides pose minimal risk to farmers, consumers, and beneficial insects. They protect pollinators like bees and beneficial predators such as ladybugs, which keep pest populations in check naturally.
✅ Reduced pesticide resistance risk
Many chemical pesticides lose effectiveness over time as pests develop resistance. Biopesticides, with their diverse and natural modes of action, help slow down this resistance buildup.
✅ Minimal residue concerns
Since biopesticides break down quickly, they leave little to no harmful residues on crops. This is a major advantage for farmers supplying organic markets or exporting to regions with strict pesticide regulations.
👉 Read more about sustainable agriculture practices on our dedicated blog on Smarter Pest Control for Better Yields
❌ Slower acting than chemical pesticides
Unlike chemical pesticides that kill on contact, many biopesticides work by disrupting pest life cycles or gradually reducing populations.
❌ Effectiveness depends on environmental conditions
Factors like temperature, humidity, and UV exposure can impact how well they work.
❌ Shorter shelf life
Biopesticides don’t last as long in storage as synthetic pesticides.
❌ May require frequent applications
Since biopesticides break down quickly in the environment, you may need multiple applications for consistent pest control.
Before diving into biopesticides examples, it’s essential to understand their three main categories. Each works differently to protect crops, and knowing their differences will help you choose the right solution for you.
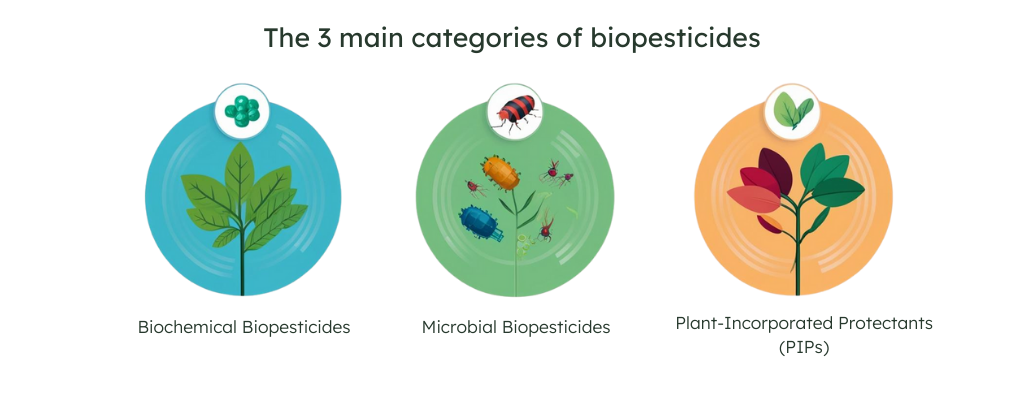
These are naturally occurring substances that control pests through non-toxic mechanisms. They can disrupt insect mating, repel pests, or interfere with their development.
Examples:
These use microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, viruses, or protozoa) to infect and kill pests. They are often highly specific to certain pests, making them safer for beneficial insects and the environment.
Examples:
💡Popular Products: Farmers commonly use Dipel DF, met52, and BotaniGard
These are genetically modified (GM) plants that produce their own pest-killing substances. Scientists insert pest-resistant genes into plants, eliminating the need for external pesticide applications.
Examples:
🔍 Looking for biopesticides? Check out Aglist.com – a trusted marketplace that helps farmers like you find, compare, and purchase biopesticides and other crop protection products.
Biopesticides can be a powerful tool in your pest management strategy, but only if used correctly.
🕐 Apply preventatively and at the right pest life stage
One of the most critical factors in biopesticide success is applying them at the right pest life stage.
They work best before pests become a major problem, but when exactly?
⏳ Applying at the wrong time can significantly reduce effectiveness.
🔍 Want to master pest timing?
👉 Check out our more in-depth blog on pest life cycle
Here are some more key tips for success:
🕐 Apply preventatively: They work best before pests become a major problem
🌦️ Check weather conditions: Some biopesticides require moisture to activate, while others degrade in sunlight
📦Store properly: Purchase only what you need and store it according to the manufacturer’s guidelines
🔄 Incorporate an IPM approach: Rotate with other controls to prevent resistance
🎯 Target the right pests: Each biopesticide is pest-specific, so choose accordingly
| What to Consider | Why? |
| Are you growing organic or conventional crops? | Biopesticides are ideal for organic farming and IPM strategies. |
| Do your main pests have effective biopesticide options? | Some pests may still require chemical treatments. |
| Can you apply preventively? | Many biopesticides work best before infestations get severe. |
| Is the biopesticide available and cost-effective for your operation? | Some products may be pricier than traditional chemical pesticides. |
| Are you looking to reduce chemical residues and protect pollinators? | Biopesticides support sustainability and soil health. |
No, biopesticides are generally safe for humans and beneficial insects. They break down quickly, leaving minimal residues. However, it’s still important to follow application guidelines.
Biopesticides use natural mechanisms to control pests. Some disrupt insect growth, and others act as repellents. Their mode of action depends on their type.
Yes! Many farmers integrate biopesticides into their IPM strategies, using them alongside chemical pesticides to reduce chemical use and delay resistance. Just check for compatibility before mixing.
Unlike chemical pesticides, most biopesticides take time to work. Some need days or weeks to reduce pest populations. That’s why early application is crucial.
No, most biopesticides target specific pests. Proper pest identification is key for choosing the right product.
Here’s how you can take this to the next level 🚀
Understanding biopesticides is the first step to safer, more sustainable pest control, but applying them effectively can still be a challenge.
Wouldn’t it be easier if you knew how to make the right decisions at the right time?
That’s where scoutlabs insect traps come in, offering:
✔ Early pest detection
✔ 93% accuracy in pest identification
✔ Smarter pesticide use
✔ Effortless monitoring
📩 Have questions? Talk with us — we’re here to help! 😊