Almond orchards are constantly under threat from a variety of pests and diseases that can weaken trees, reduce yields, and compromise nut quality. From burrowing borers to destructive fungi, these issues can significantly impact orchard productivity if not properly managed. Early detection and proactive control measures are essential to maintaining healthy trees and ensuring a profitable harvest.
In this guide, we’ll explore some of the most common almond tree pests and diseases, their symptoms, and effective prevention and control strategies to help protect your orchard.
👉 Do you have Codling Moth in your orchard and want to fight against it? Read our previous blog post
Species: Bondia comonana, Euzophera semifuneralis
These pests tunnel into tree wood, weakening branches and making them prone to breaking. They can cause long-term damage if not controlled. If left untreated, trees may suffer extensive structural damage, leading to reduced productivity and tree mortality over time.

Figure: Larvae of Euzophera semifuneralis
🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Species: Amyelois transitella
This pest is particularly damaging because it feeds on almond kernels, reducing yield and quality while also increasing susceptibility to aflatoxin contamination. Aflatoxins are toxic compounds that pose significant health risks and can make almonds unsellable if contamination levels exceed safety thresholds.
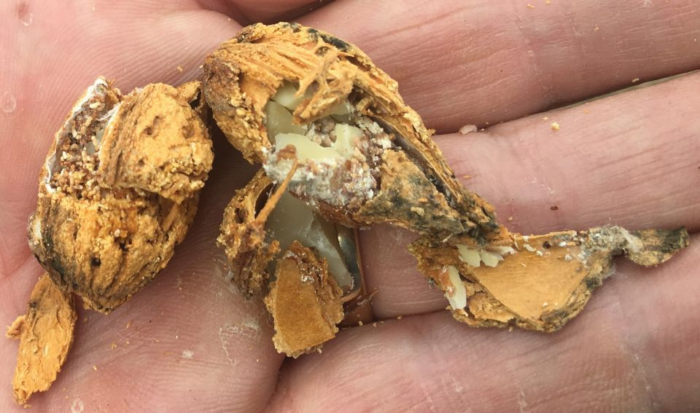

Figure: Navel orangeworm frass – Photo: Franz Niederholzer
🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Species: Cydia molesta
This pest primarily damages young shoots and fruits, leading to reduced yield and tree vigor. If left uncontrolled, it can significantly impact almond and peach production, as damaged fruits become vulnerable to secondary infections by fungi and bacteria.
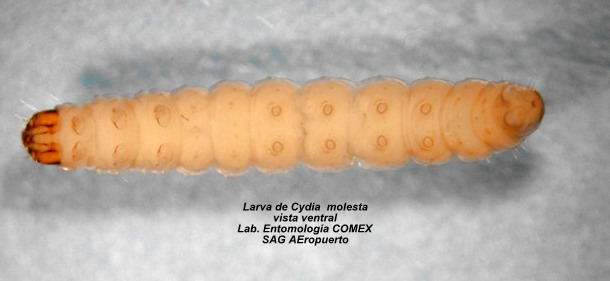
🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Species: Archips argyrospila
These caterpillars feed on leaves and buds, reducing photosynthesis and yield potential. Severe infestations can result in significant defoliation, making trees more susceptible to environmental stressors such as drought and disease.
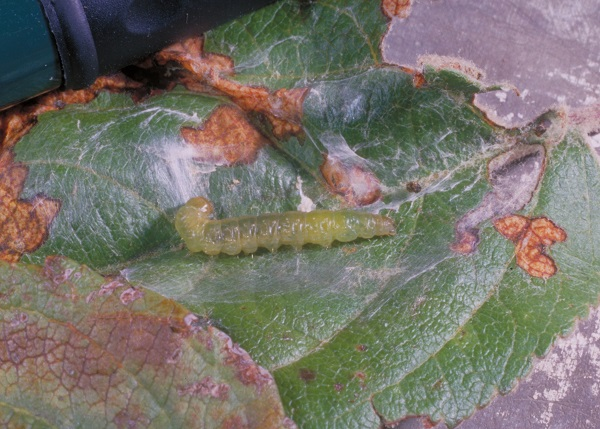
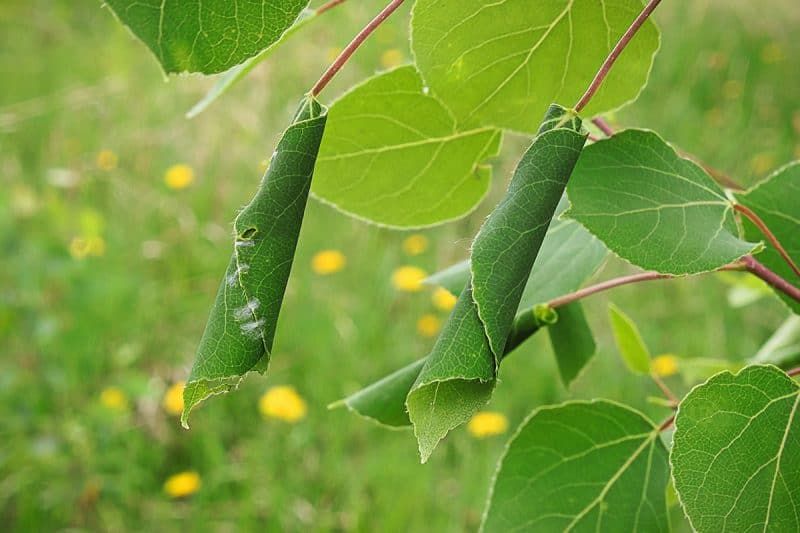


Figure: Leafroller larva and damage
🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Species: Leptoglossus spp.
These bugs pierce the almonds and suck out nutrients, leaving them weak and prone to disease. They thrive in warm conditions and orchards with plenty of ground cover. Their feeding activity also creates entry points for fungal pathogens, leading to additional crop losses.
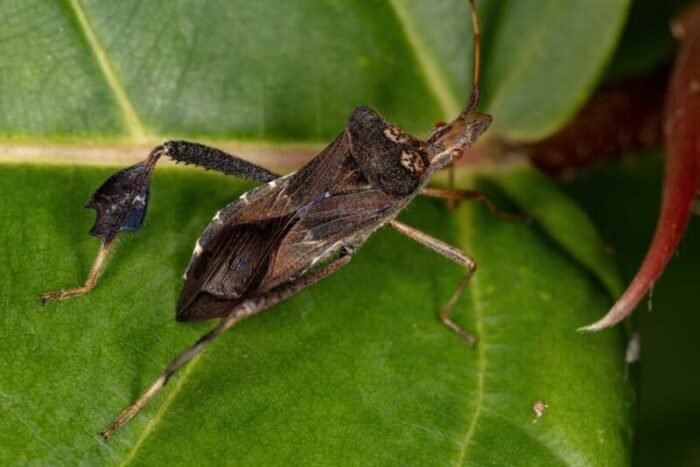


🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Species: Tetranychus spp.
These tiny pests suck nutrients from leaves, weakening the tree and making it susceptible to other stressors like drought and disease. Spider mite populations can explode under hot, dry conditions, making them a persistent problem in arid almond-growing regions.

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
👉 Do you want to learn more about insect traps? This article is for you: Insect Traps Explained
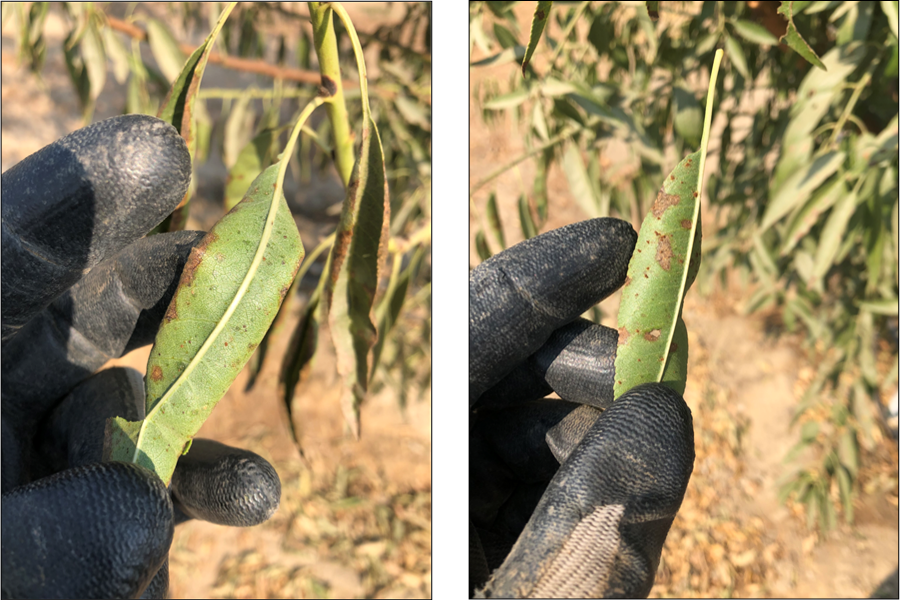
Pathogen: Coryneum beijerinekli Oud
This fungal disease thrives in humid conditions and weakens the tree by causing defoliation. Severe cases can significantly reduce photosynthesis, ultimately lowering nut production.

Figure: Rupture of Leaf
🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Pathogen: Sphaerotheca pannosa
This fungal disease affects leaves and young fruit, reducing photosynthesis and fruit development. The powdery mildew-like appearance can spread rapidly, leading to extensive crop losses if not properly managed.

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
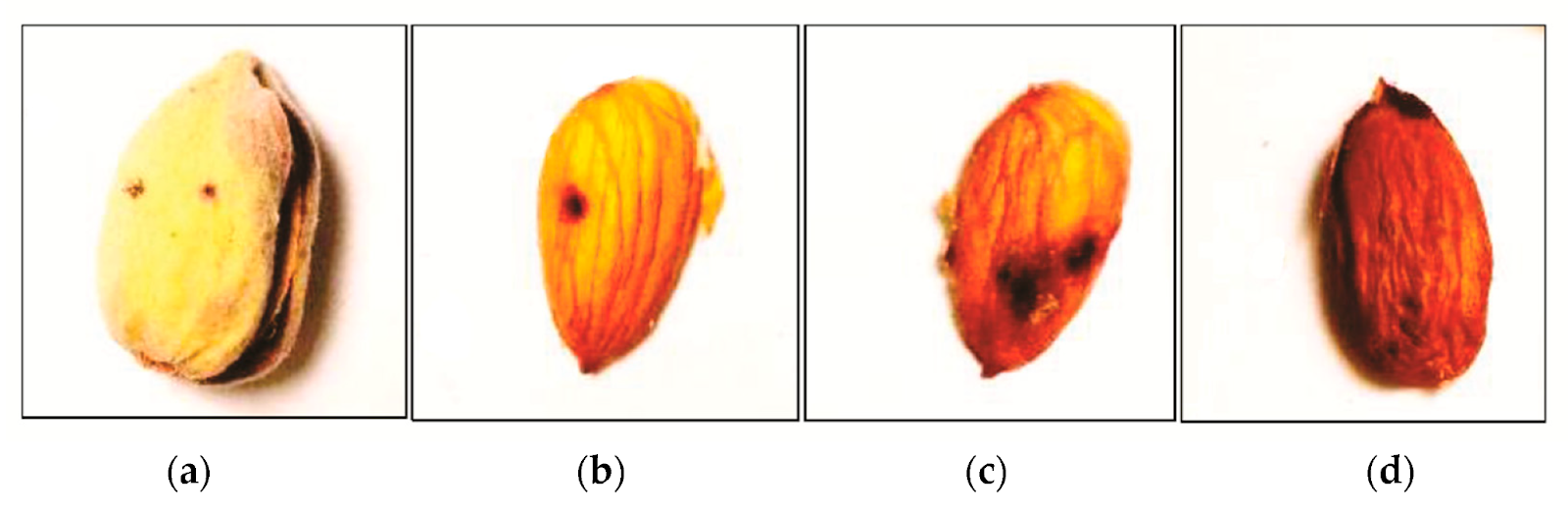
Pathogen: Colletotrichum acutatum
This fungus thrives in wet conditions and spreads rapidly, leading to severe yield losses.

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Pathogen: Verticillium dahliae
This soil-borne fungus clogs the tree’s vascular system, preventing water and nutrients from reaching the branches.

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
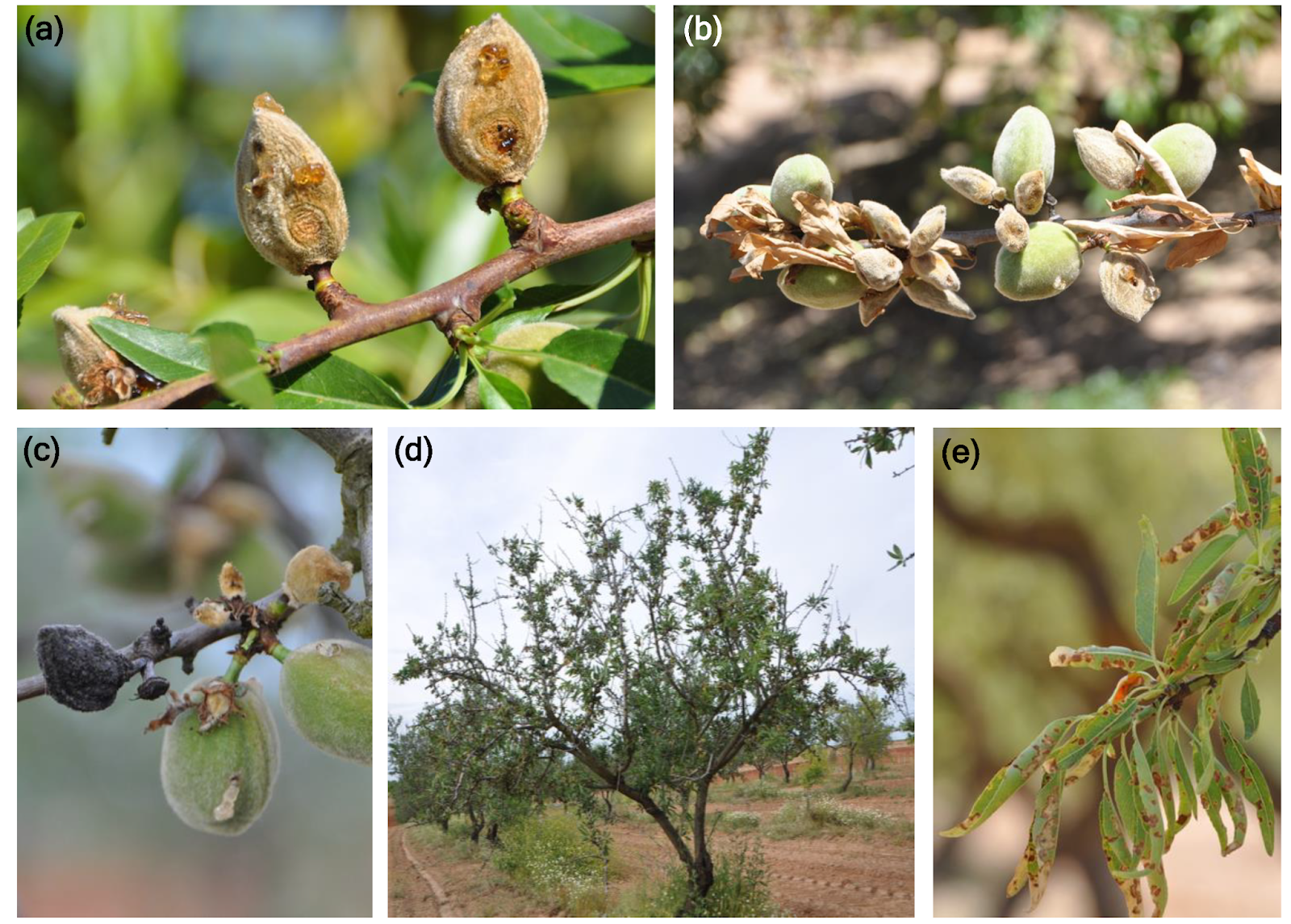
Pathogen: Wilsonomyces carpophilus
This fungal disease spreads in wet conditions and can cause significant defoliation
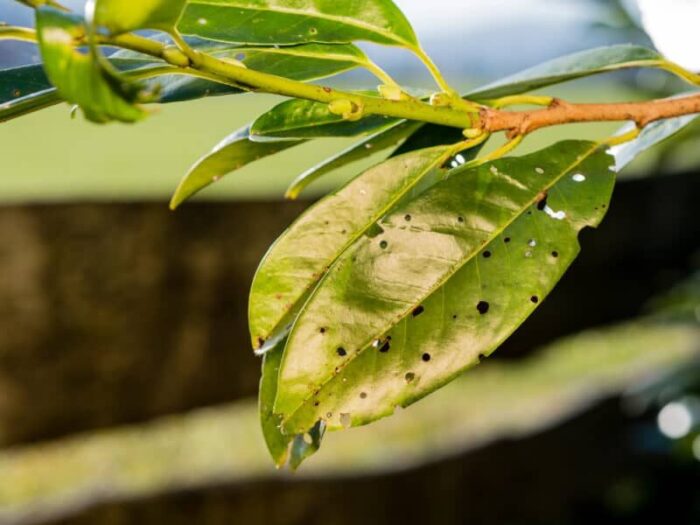

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Pathogen: Alternaria alternata
This disease thrives in warm, humid conditions and can cause significant defoliation, reducing yield potential.

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Pathogen: Monilinia laxa
This fungal disease thrives in rainy weather and spreads via airborne spores.

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Pathogen: Botrytis cinerea
This fungal disease occurs in cool, wet conditions, affecting young fruit clusters.

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Pathogen: Tranzschelia discolor
This disease reduces tree vigor and yield over time.

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
Pathogen: Phytophthora spp.
This disease is caused by soil-dwelling fungi that thrive in wet conditions.
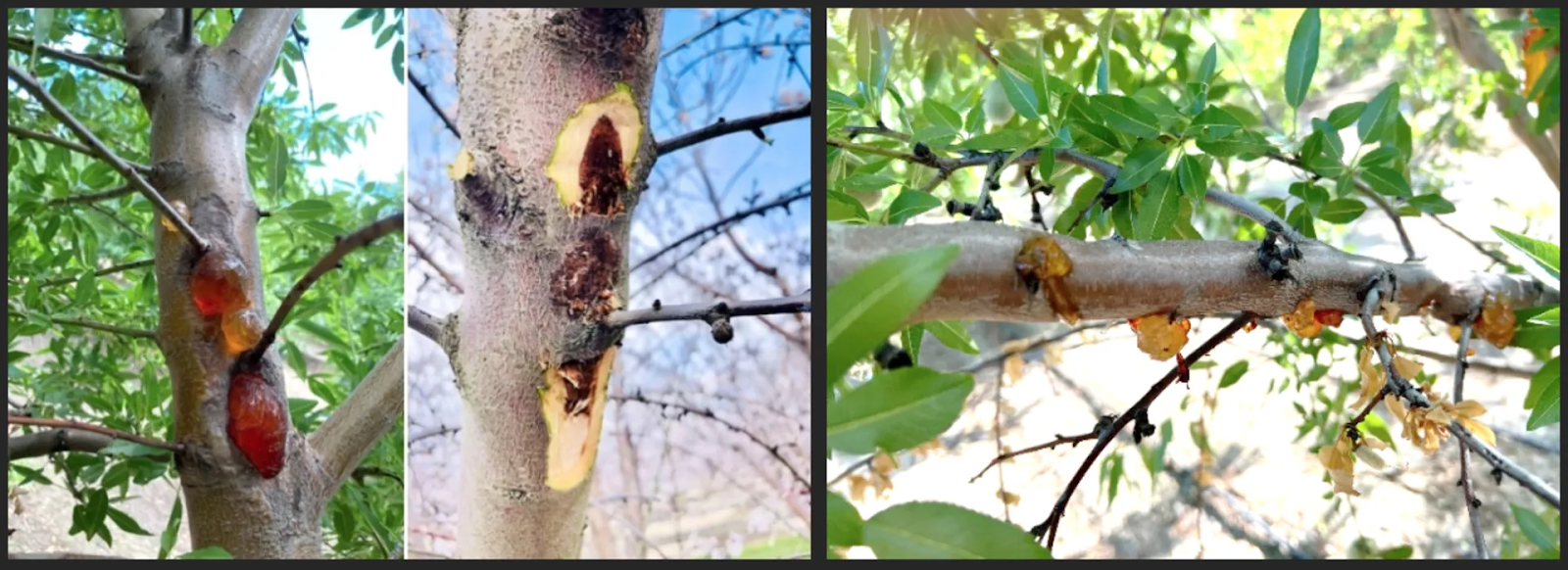

🔍 Symptoms:
💡 Prevention & Control:
👉 Looking for Integrated Pest Management solutions? Check out these 3+1 Tips for Successful Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Protecting almond orchards from pests and diseases requires a combination of vigilance, strategic interventions, and modern monitoring tools. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) techniques, including biological controls, AI-powered monitoring systems, and careful orchard sanitation, can help minimize damage while reducing reliance on chemical treatments.
By staying informed about the key threats to almond production and implementing proactive measures, growers can ensure healthier trees, higher yields, and a more sustainable farming approach. Whether you’re dealing with aggressive borers, persistent fungal infections, or opportunistic mites, a well-rounded pest and disease management plan is the best defense against crop losses.
🧐 Do you have any questions about digital traps and how we can help you detect insects? Reach out to us—we’re here to help!