In the world of modern farming, pest control is a constant battle. Farmers are seeking more sustainable, targeted ways to protect their crops from harmful insects without relying heavily on chemical pesticides. One solution that has emerged with significant promise is the use of pheromones—chemical signals used by insects to communicate.
But how exactly do these pheromones work, and what role do they play in modern pest management strategies like Integrated Pest Management (IPM)?
Insects communicate with one another by releasing small quantities of pheromones, a chemical substance that acts like a scent, into the air. Pheromones are specialized chemical signals secreted by organisms to trigger specific social responses in members of the same species. Pheromones play a vital role in various behaviors, including mating, foraging, and territory marking. Each type of pheromone serves a unique purpose, allowing insects to communicate in ways that have critical implications for their survival and reproduction.
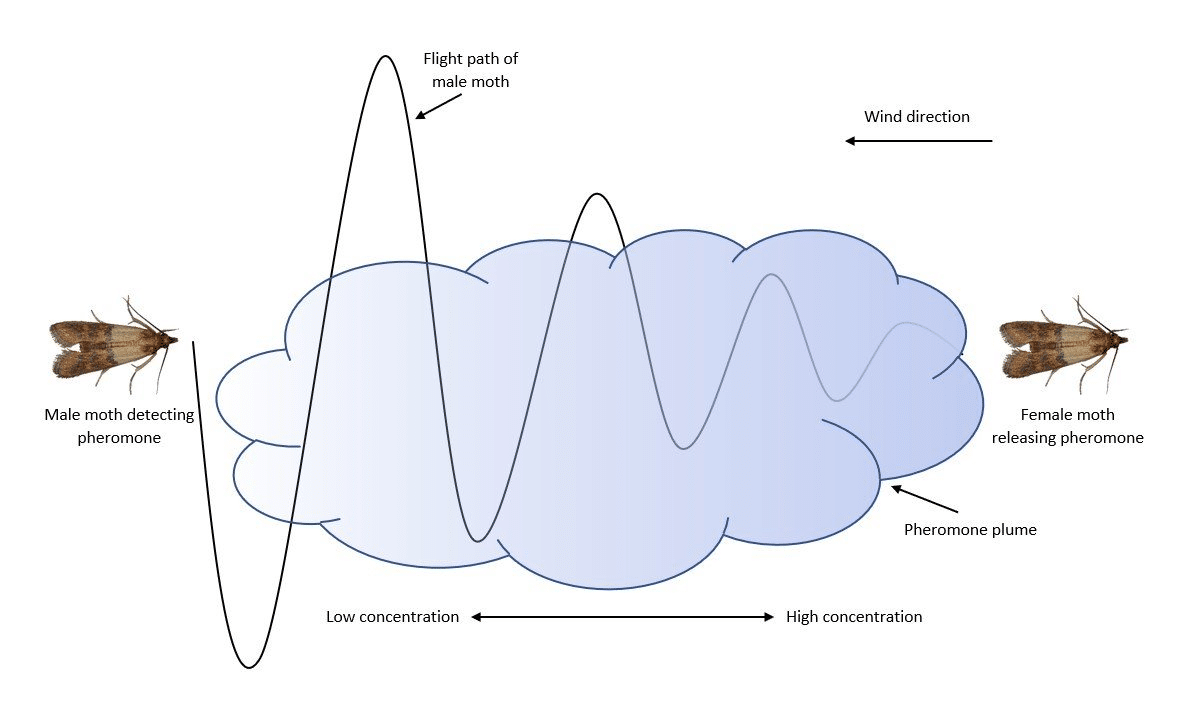
For example:
Understanding these chemical interactions offers farmers a strategic opportunity to manage pest populations without relying on toxic pesticides.
Using the right pheromones for pest control can revolutionize how you protect your crops. By disrupting the mating and behavior patterns of pests, pheromone-based solutions provide an eco-friendly, targeted approach to pest management.
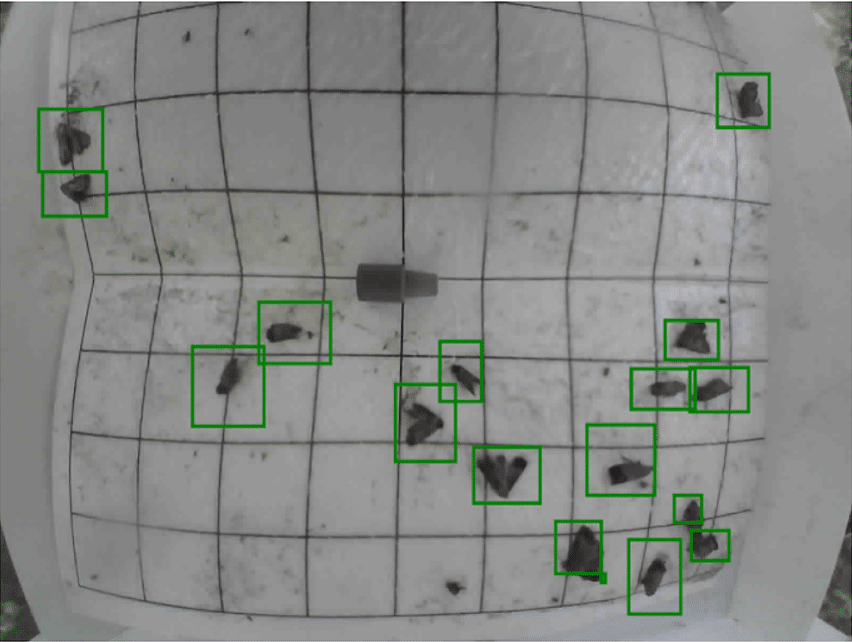
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach that uses multiple techniques to minimize pest damage while reducing chemical pesticide use. A core tactic within IPM is the use of pheromone traps, which can attract specific insect pests by mimicking natural pheromones.
Here’s how farmers use pheromones in IPM:
Unlike broad-spectrum pesticides that affect multiple species indiscriminately, pheromone-based strategies target specific pests while preserving beneficial insects and pollinators within the ecosystem.
Pheromone-based pest management offers several advantages over traditional pesticide use:
Farmers around the world are already seeing the benefits of using pheromones in pest management. For instance, pheromone traps have been successfully used to control pests like the European grapevine moth in vineyards, reducing damage and lowering the need for chemical sprays. Similarly, in apple orchards, pheromone traps have been a vital tool in managing Codling Moth populations, resulting in healthier crops and better yields.
These examples highlight how plant fly traps fit into a broader IPM framework, where the focus is on prevention, monitoring, and targeted control.
If you’re looking to adopt pheromone-based techniques to boost your pest management strategy, scoutlabs can take your Integrated Pest Management (IPM) efforts to the next level. Our advanced pheromone traps, paired with real-time data monitoring, provide farmers with the insights they need to protect their crops efficiently and sustainably.
Here’s how scoutlabs can help you seamlessly integrate pheromones into your IPM plan:
Identify target pests with precision
Don’t guess—know which pests are impacting your crops. scoutlabs’ monitoring system uses pheromone technology to pinpoint specific pest populations. Our expert team provides tailored advice based on local data, ensuring you’re targeting the right pests at the right time.
Track pest activity in real-time
Early detection is everything. With scoutlabs’ remote pheromone traps, you can monitor pest pressure as it develops, well before it becomes a costly issue. Our real-time data feeds give you timely alerts so you can act fast—keeping pest populations under control without unnecessary interventions.
Maximize results by combining tactics
scoutlabs empowers you to go beyond just traps. By combining pheromone monitoring with biological controls and habitat management, you’ll see greater impact with fewer resources. Our platform makes it easy to integrate these tools into one cohesive IPM plan, helping you lower costs and reduce chemical use while protecting beneficial insects.
As farmers look to reduce the environmental impact of pest control, pheromones offer a promising path forward. These chemical signals, used by insects for communication, provide a precise and eco-friendly way to manage pest populations. When integrated into an IPM program, pheromones can help reduce reliance on chemical pesticides, protect beneficial insects, and contribute to more sustainable farming practices.
Farmers can take a step toward a future where pest management is not only effective but also environmentally responsible. As new technologies emerge, the use of pheromones in agriculture will only become more refined, offering a powerful tool in the ongoing quest for sustainable, efficient pest control.